I've been playing PC games for decades, and for my money, few technologies have done more to make buttery-smooth performance in demanding games achievable than Nvidia's DLSS tech.
DLSS first appeared around 2018 with Nvidia's GeForce RTX 20-series Graphics cards underwent development over several years before they became truly dependable and widely optimized for numerous games. Today we have reached DLSS 4, where it seems nearly standard that contemporary PC titles with substantial visual requirements offer support for DLSS. Additionally, many such games include compatibility with AMD’s FSR and Intel’s XeSS, which serve as comparable supersampling technologies.
If you're not familiar, supersampling is one of the key technologies that helps you get higher framerates in the best PC games Around now without significantly compromising graphical quality. When it first debuted, supersampling was the main highlight of DLSS since, well, it’s reflected in the name. However, nowadays, DLSS has evolved to offer much more functionality.
To assist you in maximizing DLSS performance in your gaming sessions, we'll explore what it entails, how it functions, and ways to optimize it for your use.
What is DLSS?

DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) refers to a collection of technologies branded by NVIDIA, which leverage the capabilities of Nvidia GeForce graphics cards to enhance and optimize the performance of PC games through upscaling and smoothing techniques.
The number one thing DLSS does, in a nutshell, is render your game at a lower resolution than usual and then upscale it to your desired resolution using specialized algorithms running on Nvidia graphics cards.
Nvidia refers to this technology as Super Resolution, which generally allows your computer to produce more frames per second since the game operates at a lower resolution, reducing the strain on your system. This means your PC does not need to render as many individual pixels for each frame. The process involves Nvidia’s algorithms utilizing the Tensor Cores in your GeForce graphics card to attempt to predict how each frame would appear at a higher resolution and then create these enhanced images dynamically.
In the early years of DLSS, enabling this tech would often cause noticeable graphical distortions like fuzzy edges and blurry, hazy outlines around objects, especially in games that weren't optimized for the technology. But these days DLSS implementation is commonplace and very good, to the point that when I enable it in games like Alan Wake 2 and Cyberpunk 2077: Phantom Liberty I hardly see any distinction apart from significantly improved frame rates with less impact on my computer’s performance.
This doesn’t just mean I can play these games at a better quality than usual—with an improved frame rate compared to what I’d get without DLSS—but I’m also able to turn on advanced visual settings like superior shadow rendering, enhanced reflections, and additional features using the newest iteration of DLSS 4, all without significantly affecting game speed.
How does DLSS work now?
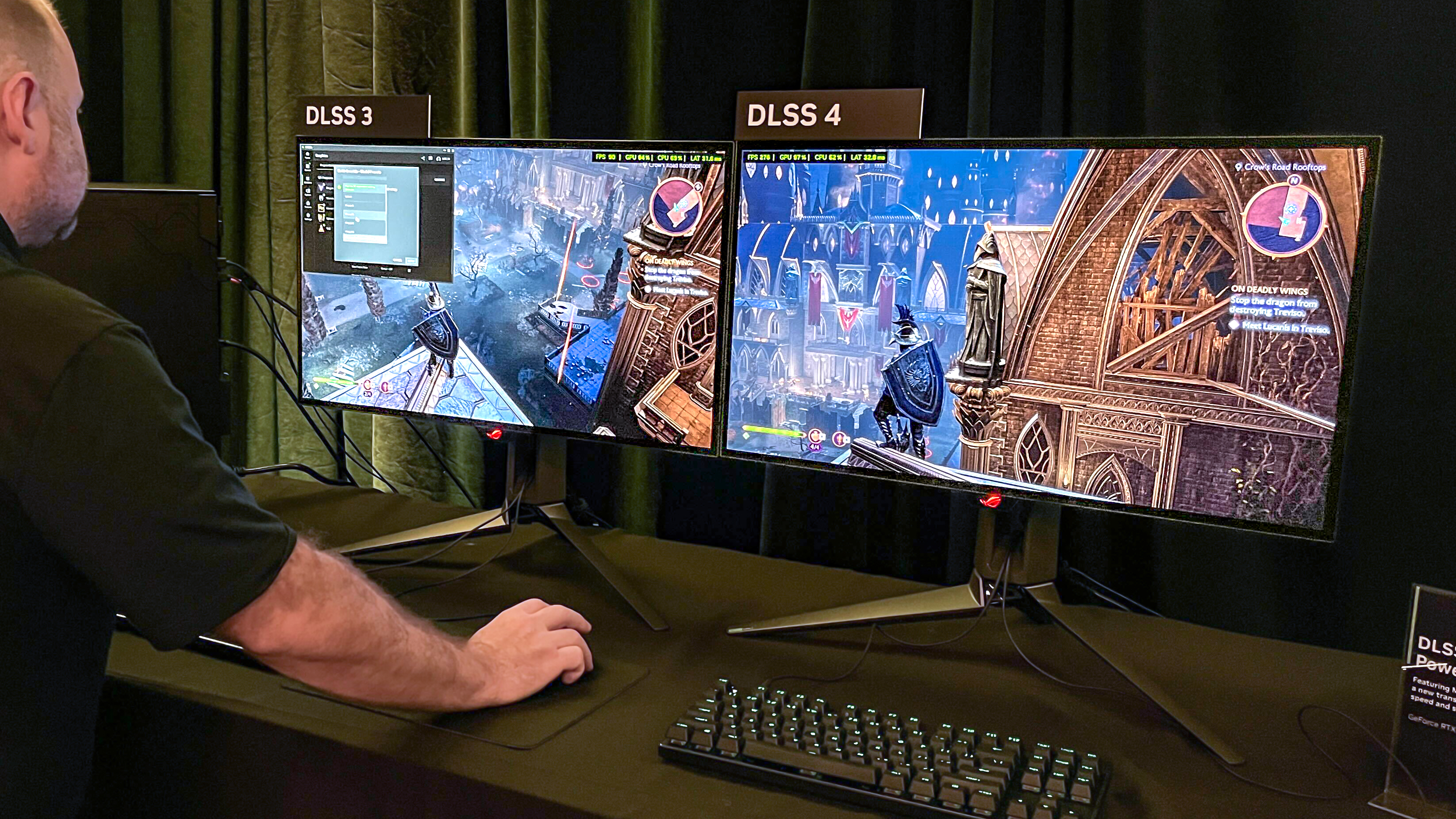

This kind of upscaling was the headline feature of DLSS at launch, but since then Nvidia has released several versions that add new features and new algorithms that let DLSS do more.
The most recent release, DLSS 4, launched alongside Nvidia's GeForce RTX 50-series graphics cards in 2025. And while there are some DLSS features that only work on specific Nvidia cards (Frame Generation is only available on 40-series and later while Multi-Frame Generation is limited to 50-series cards), most of its features will run in some form on any Nvidia card from the last five years.
One of the key changes is that Nvidia has redesigned how DLSS 4 performs upscaling through a new transformer model aimed at providing enhanced image quality with reduced blur and graphic distortions compared to previous DLSS iterations.
When the Nvidia GeForce RTX 40-series cards launched in 2023 Nvidia added another new capability to DLSS that's only available on 40-series GPUs and later: Frame Generation. When enabled in games that support it, Frame Generation works to boost your framerate by generating one additional frame for every frame your PC actually draws and renders on-screen.
The trick is, these extra frames aren't actually computed, drawn and rendered by your PC like normal — they're generated by your GPU in real time based on inferences drawn from the frames your PC is drawing, so they're effectively "AI-generated" frames. These generated frames of gameplay are sandwiched in between "real" frames of gameplay, giving you more frames per second (and thus faster, smoother gaming) without making your PC do all the work to generate them.
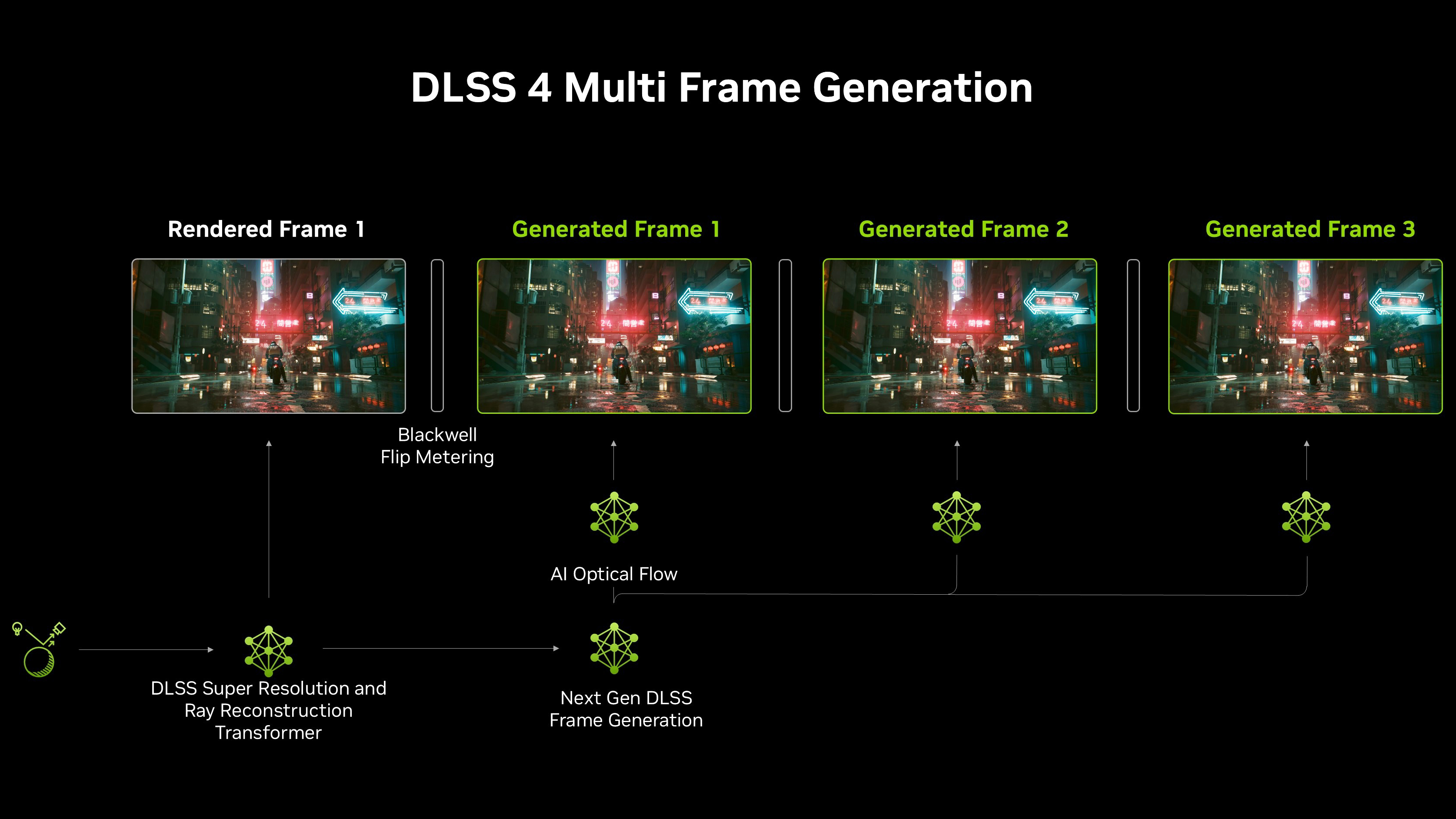
When the 50-series cards launched in 2025 they gained an exclusive upgraded version of this feature called Multi-Frame Generation. As you might guess from the name, this feature works in a similar fashion but generates 1-3 "AI" frames for every "real" frame of gameplay your PC renders.
In games that support it you can often choose between 2X, 3X and 4X Multi-Frame Generation, which tells your PC to generate one, two or three additional frames for every "real" one.
DLSS does a lot to boost framerates without costing you much in terms of graphical quality...you really do often feel like you're hitting a button and magically getting better performance with nearly no downside."
Since a game can only respond to your input as fast as it can draw a new frame of gameplay on-screen, framerate also directly affects how responsive a game feels to play.
I mention this because Multi-Frame Generation has the potential to make games feel "floaty" or less responsive because some of the frames of gameplay are being generated by looking at other frames of gameplay, rather than responding directly to what your input is telling the PC to draw on the screen.
However, there's another Nvidia feature that can help address this issue if it crops up for you: Nvidia Reflex.
When supported in a game, Nvidia Reflex can do two big things to reduce input latency and make your game feel more responsive: optimize your CPU and GPU so they're rendering frames on-screen as soon as the frame is ready, and "warp" a frame at the last second (i.e. after it's rendered but before it appears on-screen) in response to your mouse/controller input.
Finally, there's one other big thing DLSS helps with: raytracing. That's a simple term for a bundle of technologies that work together to render light bouncing around a game world in real time, which is very demanding but results in more realistic and accurate lighting (as opposed to the "baked in" pre-set lighting patterns common in most games).
Ray tracing can be enabled without DLSS in games, yet it significantly mitigates the performance hit caused by ray tracing, even for high-end systems. best gaming PCs . And with DLSS 3.5 the company added a Ray Reconstruction feature to DLSS that you can enable to have your GPU generate more pixels to fill in raytraced lighting and make it look better at a much lower performance cost.
How does DLSS impact gaming performance?
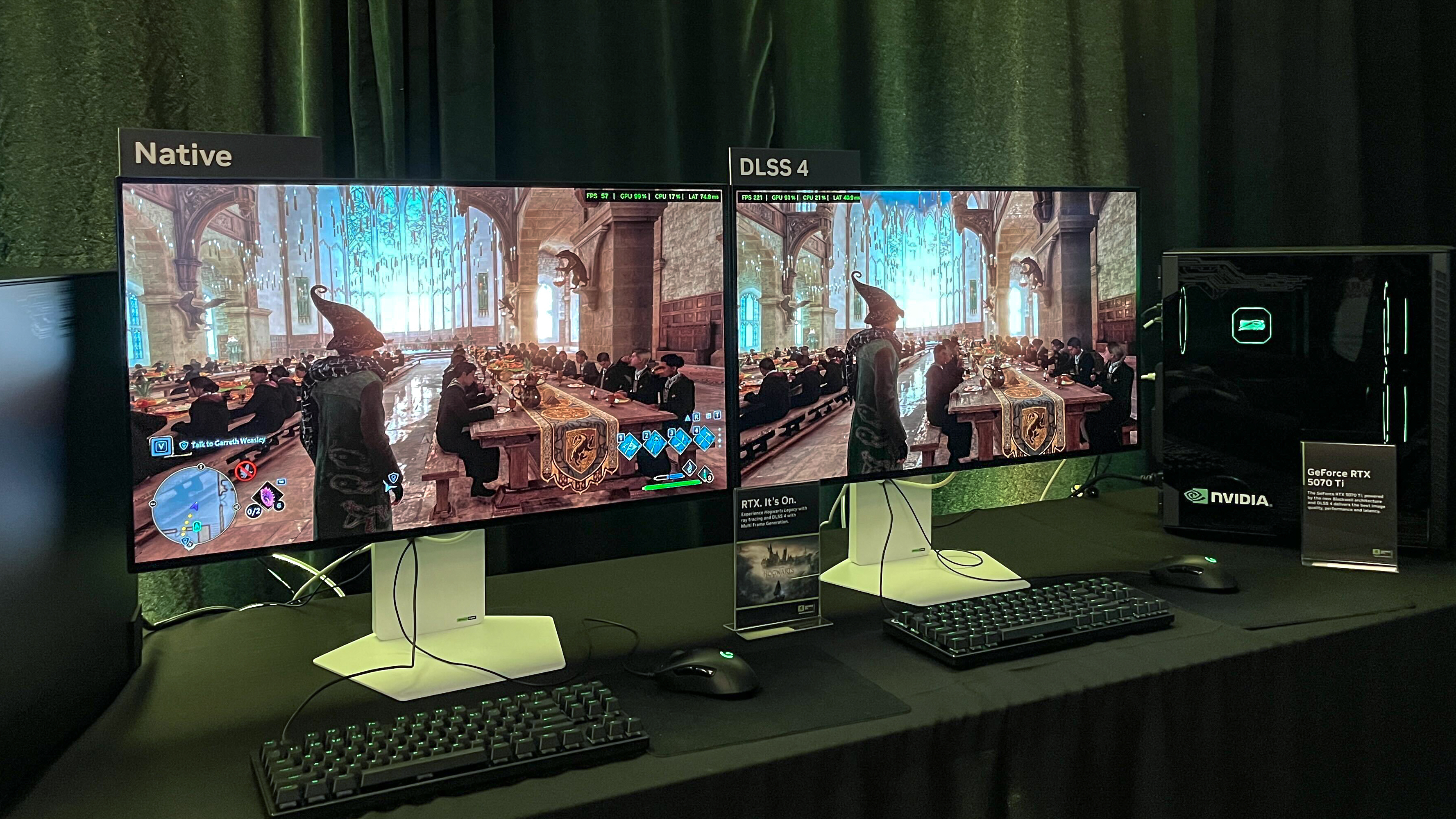

With all those features functioning well DLSS can do a lot to make games which support it look better and run smoother with very little downside.
This is why, to some degree, DLSS and comparable technologies like AMD’s FSR and Intel’s XeSS have essentially become standard practice for contemporary PC gaming—especially if your aim is to consistently enjoy playing games. best PC games at higher than 1080p and 60 frames per second.
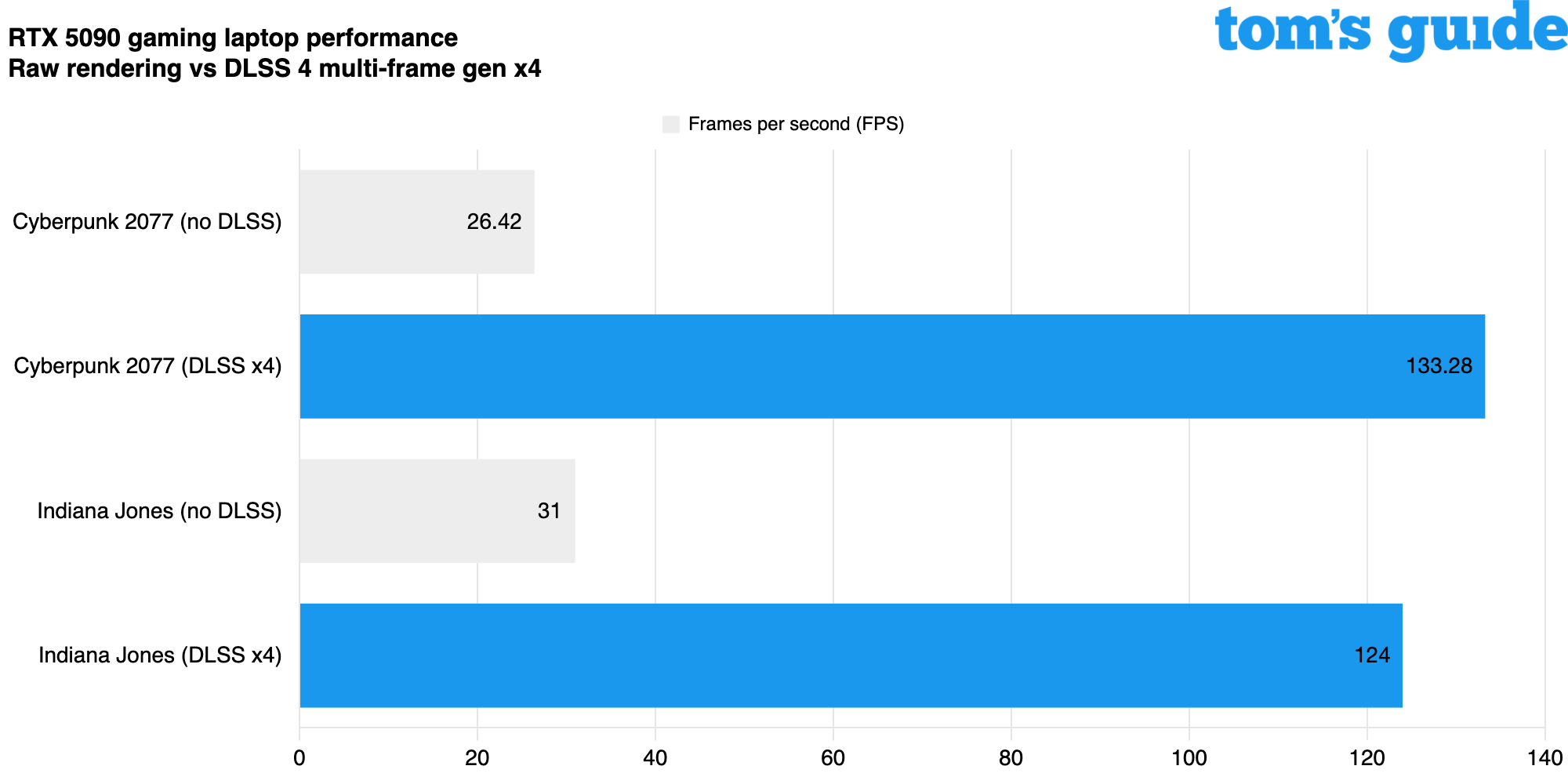
In my experience, CD Projekt Red's Cyberpunk 2077 has consistently been among the initial titles to effectively adopt and utilize newer DLSS features. Based on the test outcomes provided earlier, attempting to run this game with all settingsmaxed out on an advanced RTX 5090 gaming laptop will not enable you to maintain a steady frame rate of 60 fps.
But with DLSS 4 enabled and Multi-Frame Generation cranked to the max, you can get between 4x-5x better framerates with very little downside. Personally I don't love the way a lot of games tend to distort at 4X Multi-Frame Generation so I prefer to keep it around 2X or 3X, but Cyberpunk 2077 does a better job than most games of integrating it well.
But even in games like Assassin's Creed Mirage , Indiana Jones and F1 23 DLSS does a lot to boost framerates without costing you much in terms of graphical quality.
As you can see from our test results above, even the conservative Quality mode can give you 20-30 extra FPS in a modern game, and fine-tuning DLSS to Balanced or Performance mode nets you even smoother gameplay.
That's why GPU upscaling tech like DLSS has become such a cornerstone of modern PC gaming: algorithms are getting good enough that you really do often feel like you're hitting a button and magically getting better performance with nearly no downside.
Currently there are over 500 games and apps that support Nvidia's DLSS tech, and many also support similar technologies from competitors AMD and Intel. So if you're not already using this stuff, I recommend you get acquainted with it — your PC gaming will never be the same.
More from Tom's Guide
- I was skeptical of RTX 50 GPUs but now I'm a believer
- Where to buy RTX 5090, 5080 and 5070 Ti gaming laptops
- I review gaming PCs for a living, and I'd never buy the RTX 5090 — here's why
Like this article? For more stories like this, follow us on MSN by clicking the +Follow button at the top of this page.
0 Response to "Nvidia's DLSS is a game-changer for PC gaming - here's how it works"
Post a Comment